The Ultimate Guide to Sleep Disorders: Causes, Symptoms, Treatments, and Prevention
Sleep is an essential component of health and well-being. Yet, for millions around the world, sleep disorders disrupt this critical function, affecting their physical health, mental clarity, and quality of life. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about sleep disorders, covering their types, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatments, and prevention strategies. Whether you’re looking to understand your own sleep challenges or help someone else, this resource has you covered.
Visit our website at www.meditation.doctor for more resources and expert guidance on improving sleep and overall wellness.
Overview of Sleep Disorders
What Are Sleep Disorders?
Sleep disorders encompass a range of conditions that interfere with your ability to sleep well. These conditions may impact:
-
Quality: How restful your sleep is.
-
Duration: How long you sleep.
-
Timing: When you fall asleep and wake up.
Sleep disorders are more than occasional sleep problems. They are chronic conditions that can lead to serious health issues if left untreated. Common symptoms include trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or feeling excessively tired during the day despite adequate rest.
Key Categories of Sleep Disorders
The International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD-3R) categorizes sleep disorders into several groups:
-
Insomnia: Difficulty falling or staying asleep.
-
Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders: Conditions affecting breathing during sleep, such as sleep apnea.
-
Central Disorders of Hypersomnolence: Excessive sleepiness, such as narcolepsy.
-
Circadian Rhythm Sleep-Wake Disorders: Misalignment of the internal body clock with external cues.
-
Parasomnias: Abnormal behaviors or experiences during sleep, such as sleepwalking.
-
Sleep-Related Movement Disorders: Conditions like restless legs syndrome.
How Common Are Sleep Disorders?
Over 50 million Americans and more than 100 million individuals worldwide suffer from sleep disorders. Despite their prevalence, many cases remain undiagnosed or untreated.
Why Is Sleep Important?
Sleep is crucial for:
-
Physical restoration
-
Memory consolidation
-
Emotional regulation
-
Immune system health
-
Metabolic balance
Common Types of Sleep Disorders
1. Insomnia
-
Description: Persistent difficulty falling or staying asleep.
-
Symptoms: Trouble initiating sleep, frequent nighttime awakenings, and waking up too early.
-
Causes: Stress, anxiety, depression, poor sleep habits, or underlying medical conditions.
-
Treatment: Cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), relaxation techniques, and sleep hygiene improvements.
2. Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
-
Description: A condition where the airway becomes blocked during sleep, causing repeated breathing interruptions.
-
Symptoms: Snoring, choking or gasping sounds during sleep, and daytime fatigue.
-
Causes: Obesity, anatomical abnormalities, and muscle relaxation during sleep.
-
Treatment: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) machines, weight loss, or surgical interventions.
3. Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)
-
Description: An uncontrollable urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations.
-
Symptoms: Tingling, itching, or crawling feelings, especially at night.
-
Causes: Genetic factors, iron deficiency, and certain neurological conditions.
-
Treatment: Medications, iron supplements, and lifestyle changes.
4. Narcolepsy
-
Description: A chronic neurological disorder causing excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks.
-
Symptoms: Cataplexy (sudden muscle weakness), hallucinations, and sleep paralysis.
-
Causes: Loss of hypocretin-producing neurons in the brain, often due to genetic predisposition.
-
Treatment: Stimulants, antidepressants, and scheduled naps.
5. Parasomnias
-
Description: Abnormal activities during sleep.
-
Types:
-
Sleepwalking: Walking or performing activities while asleep.
-
Night Terrors: Intense episodes of fear during sleep.
-
REM Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD): Acting out dreams physically.
-
-
Treatment: Ensuring a safe sleep environment, addressing underlying conditions, and using medications like clonazepam.
6. Circadian Rhythm Sleep-Wake Disorders
-
Description: Misalignment between internal body clocks and external cues.
-
Examples:
-
Delayed Sleep Phase Syndrome (DSPS): Difficulty falling asleep until late at night.
-
Shift Work Disorder: Trouble sleeping due to irregular work hours.
-
-
Treatment: Light therapy, melatonin supplements, and structured routines.
Symptoms and Causes of Sleep Disorders
Common Symptoms
-
Difficulty falling asleep
-
Frequent nighttime awakenings
-
Excessive daytime sleepiness
-
Snoring or choking during sleep
-
Unexplained mood changes
-
Difficulty concentrating or memory problems
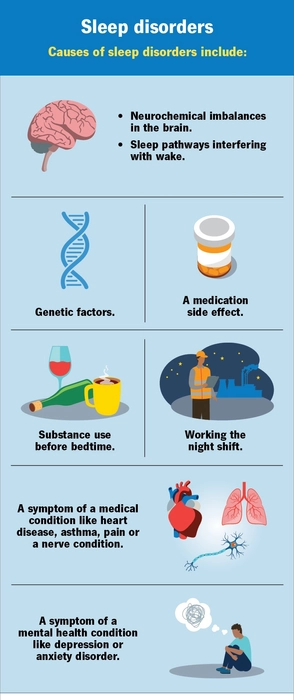
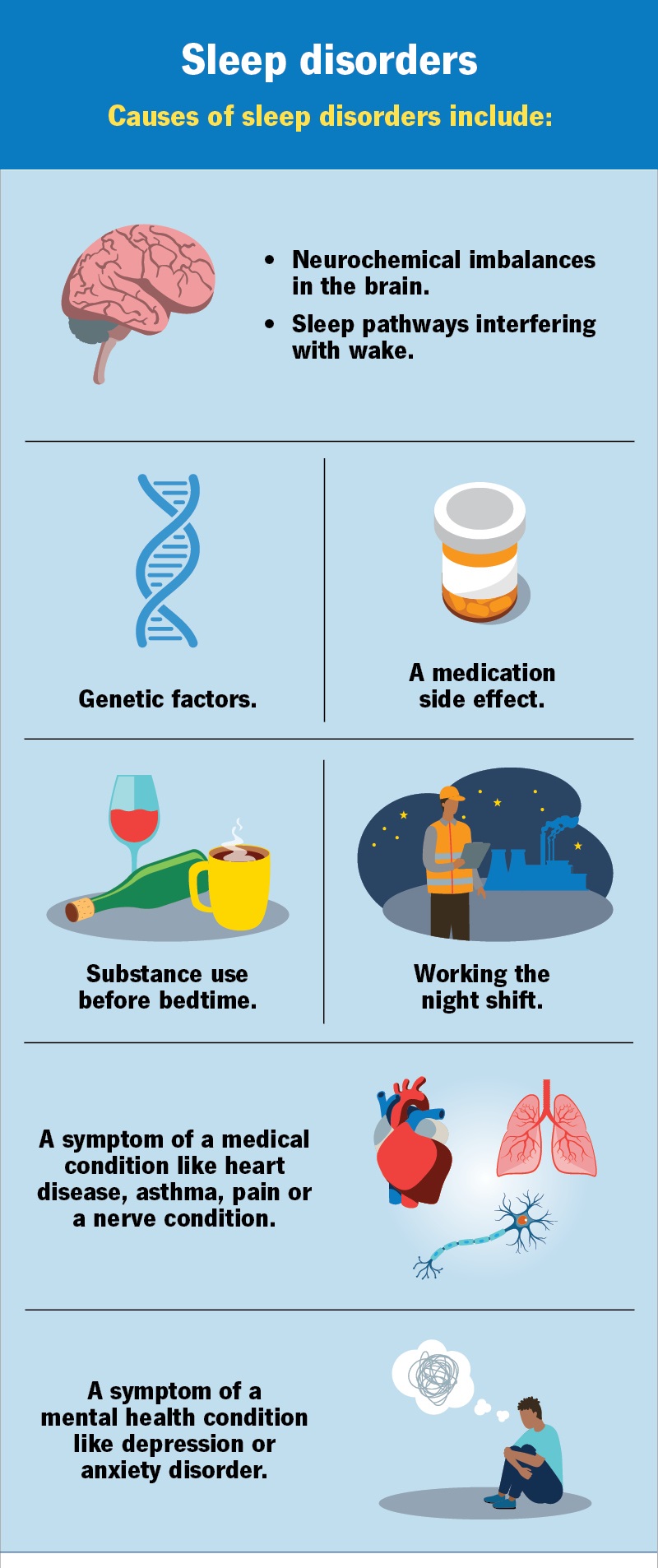
Causes
-
Medical Conditions: Heart disease, asthma, chronic pain.
-
Mental Health Issues: Anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
-
Lifestyle Factors: Irregular work schedules, substance use, or poor sleep hygiene.
-
Genetics: Family history of sleep disorders.
-
Neurological Factors: Imbalances in brain chemicals or minerals.
Diagnosing Sleep Disorders
Steps in Diagnosis
-
Medical History and Physical Examination
-
Review of symptoms and health history.
-
Discussion of sleep patterns and lifestyle factors.
-
-
Sleep Diary
-
A log of sleep habits, including bedtime, wake time, and quality of sleep.
-
-
Sleep Studies
-
Polysomnography: An overnight test monitoring brain activity, breathing, and movements.
-
Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT): Measures how quickly you fall asleep during the day.
-
-
Specialist Consultation
-
Referral to a sleep specialist for complex cases.
-
Questions to Expect
-
How many hours do you sleep per night?
-
Do you wake up feeling refreshed?
-
Do you experience snoring or gasping during sleep?
-
Do you take naps during the day?
-
Have you tried any treatments for your sleep issues?
Treatments for Sleep Disorders
Behavioral and Lifestyle Modifications
-
Maintain a consistent sleep schedule.
-
Create a relaxing bedtime routine.
-
Limit screen time before bed.
-
Avoid caffeine, alcohol, and heavy meals close to bedtime.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
-
Helps address negative thoughts and behaviors affecting sleep.
-
Effective for insomnia and other sleep-related issues.
Medications and Supplements
-
Insomnia: Melatonin, zolpidem, eszopiclone.
-
RLS: Gabapentin, pregabalin.
-
Narcolepsy: Modafinil, sodium oxybate.
Medical Devices and Interventions
-
CPAP Machines: For sleep apnea.
-
Oral Appliances: To maintain open airways.
-
Surgery: For severe anatomical obstructions.
Prevention Strategies
Good Sleep Hygiene
-
Stick to a consistent sleep and wake schedule.
-
Optimize your sleep environment (dark, cool, and quiet).
-
Avoid naps longer than 20 minutes during the day.
Stress Management
-
Practice mindfulness and meditation.
-
Engage in regular physical activity.
-
Avoid overthinking or worrying at bedtime.
Avoid Triggers
-
Limit exposure to blue light from screens.
-
Avoid stimulants like caffeine or nicotine before bed.
-
Manage chronic health conditions effectively.
Living With Sleep Disorders
Impact on Daily Life
Sleep disorders can:
-
Reduce productivity and focus.
-
Affect relationships due to mood swings or fatigue.
-
Increase the risk of accidents.
When to Seek Help
-
Persistent trouble sleeping despite lifestyle changes.
-
Excessive daytime fatigue impacting daily activities.
-
Symptoms of sleep apnea, such as loud snoring or choking.
Conclusion
Sleep disorders are complex but manageable with the right approach. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments can empower you to take control of your sleep health. If you’re struggling with sleep, visit www.meditation.doctor for expert advice, resources, and support. Together, we can help you achieve restful and rejuvenating sleep for a healthier life.